A transistor is a three terminal device, having emitter, base and
collector as its three terminals. The transistor comes in either plastic
or metal-can package. Metal-can packaged transistor can withstand more
current than a plastic packaged transistor.
A plastic packaged transistor(BC548)
To identify the terminals, hold the transistor such that its flat side
faces us and its terminals point upwards. Normally the middle terminal
will be the base (sometimes it might be collector). The transistor we
used here is an N-P-N transistor. We will discuss how to identify the
terminals of the N-P-N transistor. Similar procedure can be followed for
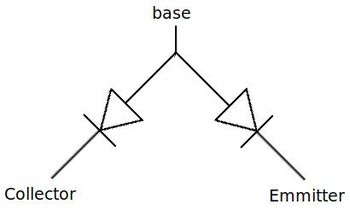
a P-N-P transistor. An N-P-N transistor can be modeled as 2 back to
back connected p-n junction diodes as shown below:
An NPN transistor modeled as back to back connected diodes.
Thus, same procedure that we followed for testing a diode(available on our previous post)
can also be used for a transistor (In this case we have 2 diodes to
test and both shouldn’t be faulty). If the transistor is not faulty,
note down the two forward resistance values measured between base and
other two terminals. The resistance of a semiconductor is inversely
proportional to its doping concentration and in a transistor, emitter is
heavily doped, base is moderately doped and collector is lightly
doped.
PS: Here is the magic equation.
Hence the forward resistance measured between base and emitter should be
less than that measured between base and collector. With this
knowledge, identify the emitter and collector using the resistance
values we noted down before. In our case the order is emitter base and
collector from right to left. REMEMBER that we identified the terminals
with them pointing upwards so while using the transistor on a
breadboard, make sure that opposite convention is followed (emitter base
and collector from left to right).
Resistance measured between base and left terminal(Emitter)
Resistance measured between base and right terminal(Collector)
Note that, Since 739 Ω <743 Ω , the terminal left to the base is emitter and the terminal right to it is collector.
In Metal can types, the pins are
arranged circularly. Just see a Tab in the rim. Hold the transistor such
that the tab faces us and terminals point upwards. The same procedure
can be followed to test the transistor.





No comments:
Post a Comment